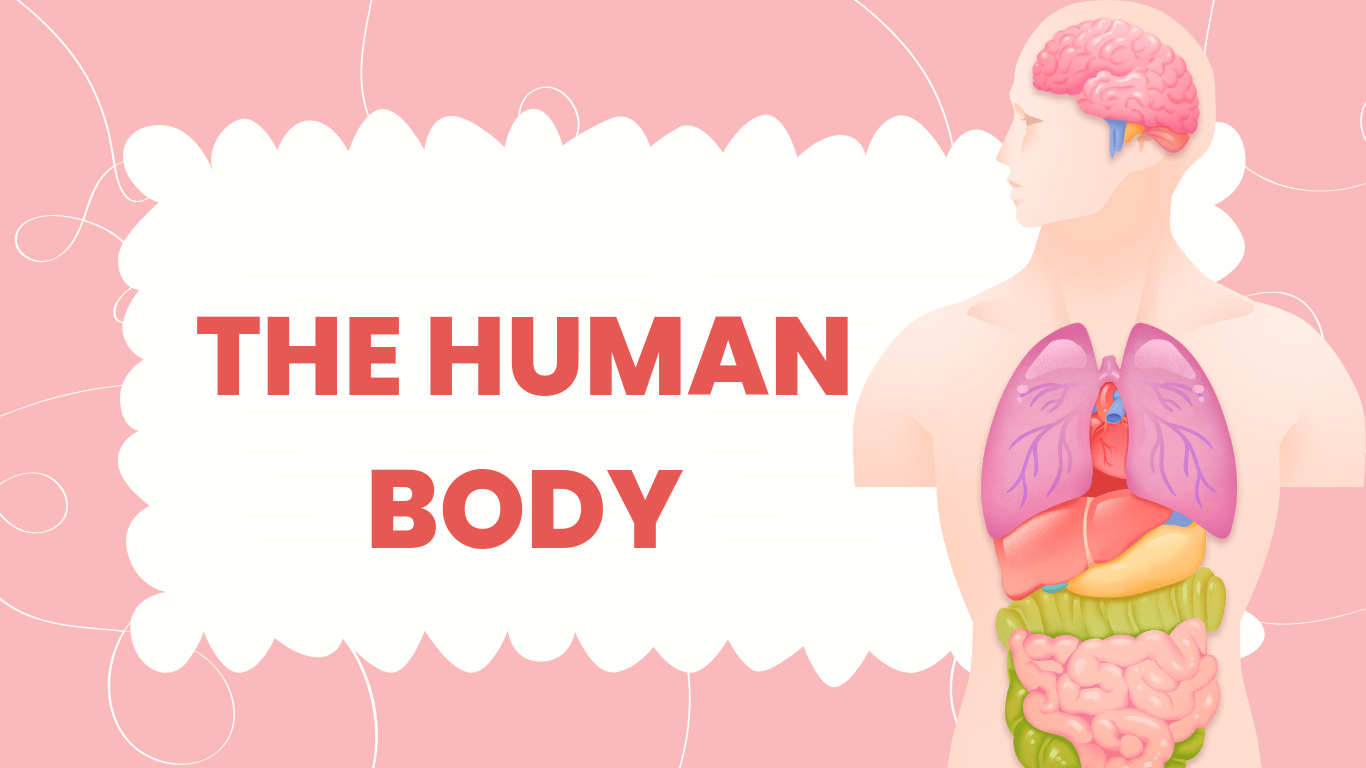
The human body generally consists of the internal and external parts. The internal parts are hidden inside of the body and cannot be seen unless through special cases such as operations. The internal part of the human body consists of organs that ensures the smooth functioning of the body.
WORDS ASSOCIATED WITH HUMAN INTERNAL BODY SYSTEM
The following are words and phrases associated with the human internal body system as well as their meaning
- Organs: Specialized structures within the body that perform specific functions, such as the heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, and brain. Each organ is part of a system, working together to maintain homeostasis and overall health.
- System: A group of organs and tissues that work together to carry out a particular function or set of functions in the body. Examples include the nervous system, circulatory system, and digestive system.
- Nervous: Refers to the nervous system, which includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body, enabling movement, sensation, and coordination.
- Skeletal: Refers to the skeletal system, which consists of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints. This system provides structure to the body, protects vital organs, and allows movement.
- Respiratory: Relates to the respiratory system, which includes the lungs, trachea, and bronchi. It is responsible for the exchange of gases, primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the body and the environment.
- Excretory: Refers to the excretory system (or urinary system), which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. This system removes waste products and excess substances from the body, primarily through urine.
- Intestine: Refers to the small intestine and large intestine, which are part of the digestive system. The small intestine absorbs nutrients from digested food, while the large intestine absorbs water and forms solid waste.
- Lungs: Paired organs in the respiratory system that are responsible for gas exchange. They take in oxygen from the air and expel carbon dioxide from the blood.
- Heart: A muscular organ in the circulatory system that pumps blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products.
- Digestive: Refers to the digestive system, which includes organs like the stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, pancreas, and others. It breaks down food into nutrients and absorbs them into the bloodstream.
- Metabolism: The set of chemical reactions that occur within cells and organisms to maintain life. It involves the breakdown of nutrients to produce energy (catabolism) and the building of cellular structures (anabolism).
- Cells: The basic structural and functional units of the body. Every organ, tissue, and system in the body is made up of cells, which carry out the body’s processes.
- Circulatory: Refers to the circulatory system, which includes the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It transports nutrients, oxygen, and waste products throughout the body.
- Endocrine: Refers to the endocrine system, which consists of glands like the thyroid, pituitary, and adrenal glands. It secretes hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and various bodily functions.
- Blood Vessel: Tubular structures, including arteries, veins, and capillaries, that carry blood throughout the body. Blood vessels are part of the circulatory system.
- Vein: A type of blood vessel that carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart, except for the pulmonary veins, which carry oxygenated blood from the lungs.
- Arteries: Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the rest of the body, except for the pulmonary arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
- Reproductive: Refers to the reproductive system, which includes the organs responsible for producing offspring. In females, this includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina. In males, it includes the testes, prostate, and penis.
- Trachea: The windpipe, a tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi, allowing air to pass from the mouth and nose to the lungs.
- Oesophagus: A muscular tube that connects the throat (pharynx) with the stomach. It carries food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach.
- Windpipe: Another name for the trachea, which is part of the respiratory system and conducts air to and from the lungs.
- Kidney: A pair of organs in the excretory system that filter waste from the blood to form urine. The kidneys also regulate blood pressure, electrolytes, and red blood cell production.
- Liver: An organ in the digestive system that processes nutrients, detoxifies harmful substances, and produces bile to help digest fats.
- Alimentary Canal: The long tube in the digestive system that runs from the mouth to the anus. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum. It is responsible for the digestion and absorption of food.
- Digestive Tract: Another term for the alimentary canal, which involves the process of digestion and absorption, as well as the elimination of waste.
SEE ALSO:
- Words associated with home and family life
- Words associated with Agriculture
- Words associated with fishing
- Words associated with Traditional religion
- Words associated with Christian religion
- Words associated with Islamic religion
- Words associated with HIV/AIDS
- Words associated with Advertising
- Words associated with Stock Exchange
- Words associated with Animal Husbandry
- Words associated with Health and Health care